What is a
Hernia?
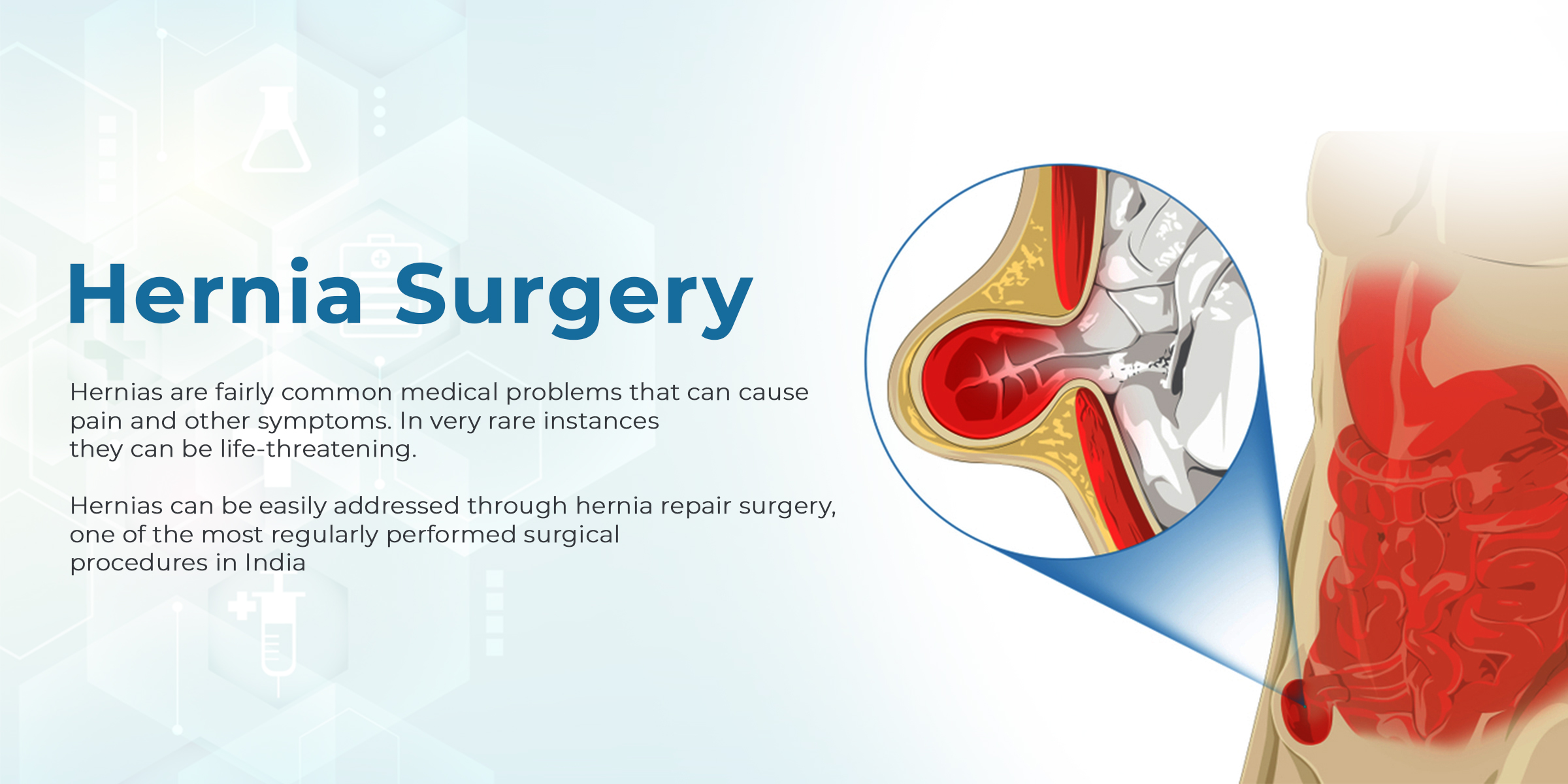
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a hole or weak point in the surrounding muscle or tissue. There are several types, but they all occur in the abdomen or groin areas. Hernias are not always easy to detect, and sometimes you may not realize you have one until a doctor finds it during a routine physical.
In many cases, hernias do not have symptoms, and at first, they may not affect your life at all. While you can live with the condition untreated for some time, it is important to have the issue repaired before more serious health issues develop. The only effective method of hernia repair is surgery.
Types of
Hernia
Inguinal Hernia
Umbilical Hernia
Ventral Hernia
Incisional Hernia
Divarication
Hiatus Hernia
Diaphragmatic Hernia
Causes of
Hernia
Post Surgeries
Wound Infections

Post Pregnancy
Regularly Lifting Heavy Weight

Chronic Coughing

Advanced Age
Congenital

Obesity

Urine and Stool Obstruction
The Benefits of
Hernia Repair
Principle of Surgery
Hernias are usually detected because they result in noticeable bulges around the abdomen or groin. Surgery involves pushing the organ or tissue back into place.

Relieve Pain
Hernias can be tender to the touch and cause severe discomfort while performing normal daily activities.

Reduce Chance of Complications
While hernias are relatively benign at first, they can lead to serious issues in the future, such as intestinal incarceration or bowel obstruction, which can be life-threatening.
Types of
Procedures
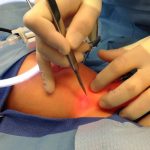
Laparoscopic inguinal Hernia Repair
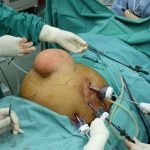
Open umbilical hernia repair
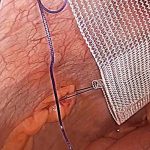
Laparoscopic incisional hernia repair
Abdominal wall
Reconstruction

Laparoscopic hernia repair is a technique to fix defects in the abdominal wall using small incisions, Laparoscopes (small telescopes inserted into the abdomen) and a patch (mesh) to reinforce the abdominal wall.
Advantages of
Laparoscopic Surgical Procedure
Less Surgical Scarring
With laparoscopic surgery, a few small incisions are made around the abdomen and the surgeon works through these tiny incisions. There is little to no visible scarring after hernia surgery.

Less Pain Procedure
Laparoscopic surgical techniques combined with sedation and anesthesia eliminates pain during the operation. The small incisions, removal and careful adjustment of tissues also minimize post-op soreness and related side effects.

Safer, More Precise Treatment
The tiny surgical tools in the surgery are extremely precise. The surgeon can manipulate the equipment with great accuracy. The affected tissues are treated without harming the surrounding tissue.
Faster Recovery Times
Laparoscopic surgery avoids the large incisions of open surgery. Patients will have shorter hospital stays or go home the same day.